- EUR/USD moves higher to near 1.1350 as the US Dollar faces selling pressure ahead of the Fed’s monetary policy meeting on May 6-7.
- US President Trump said he is confident about closing trade deals this week.
- The ECB is expected to continue lowering interest rates despite the increase in Eurozone inflation in April.
EUR/USD climbs to near 1.1360 during the North American trading hours on Monday after recovering from the three-week low of 1.1265 posted last week. The major currency pair gains as the US Dollar (USD) slumps on persistent uncertainty over United States (US)-China trade relations and as investors turn cautious ahead of the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) monetary policy announcement on Wednesday.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, drops to near 99.50 but is trading inside Friday’s range.
Over the weekend, US President Donald Trump expressed confidence while speaking with reporters that bilateral trade deals with some of his trading partners could be announced this week. However, he confirmed not having any dialogue with Chinese leader Xi Jinping this week, but didn’t deny any ongoing trade discussions between officials from both nations.
While the announcement of bilateral trade deals by Washington would indicate that fears of tariffs proposed by US President Trump have peaked now, the long-lasting standoff between the world’s two largest powerhouses will continue to keep investors on their toes.
This week, the major trigger for the US Dollar will be the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) monetary policy meeting, which will be announced on Wednesday. The Fed is widely anticipated to leave interest rates unchanged in the range of 4.25%-4.50%. Therefore, investors will pay close attention to the monetary policy statement and Fed Chair Jerome Powell’s press conference to get cues about the interest rate outlook.
Better-than-expected Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) data for April and elevated consumer inflation expectations in the face of Donald Trump’s tariff policy will be a limiting factor for the Fed to reduce interest rates.
Daily digest market movers: EUR/USD gains ahead of US Services PMI
- EUR/USD at the expense of the US Dollar (USD). The Euro (EUR) trades broadly flat while traders are increasingly confident that the European Central Bank (ECB) will reduce interest rates again in the June policy meeting despite hotter-than-expected Eurozone Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP) data for April.
- The data showed on Friday that the core HICP – which excludes volatile components like food, energy, alcohol, and tobacco – grew at a faster pace of 2.7% compared to estimates of 2.5% and the March reading of 2.4%. In the same period, the headline HICP rose steadily by 2.2% on year, faster than estimates of 2.1%.
- Traders continue to bet on more interest rate cuts from the ECB as they are more concerned about the Eurozone economic outlook due to the fallout of Donald Trump’s protectionist policy than the slight increase in inflationary pressures.
- On Friday, ECB Vice President Luis de Guindos expressed confidence in an interview with Austria’s Die Presse newspaper that the central bank could continue reducing interest rates, Reuters reported. “It depends on how inflation develops. But we can be optimistic here,” de Guindos said, after being asked how long the ECB will continue reducing interest rates.
- During European trading hours, the Eurozone Sentix Investor Confidence Index improved to -8.1 in May following April’s -19.5 despite growing economic risks from Trump’s international policies.
- In Monday’s session, the EUR/USD pair will be influenced by the US final S&P Global and ISM Services Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) data for April. The ISM Services PMI is expected to come in lower at 50.6 from 50.8 in March, signaling that the services sector grew at a moderate pace.
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD recovers from 20-day EMA
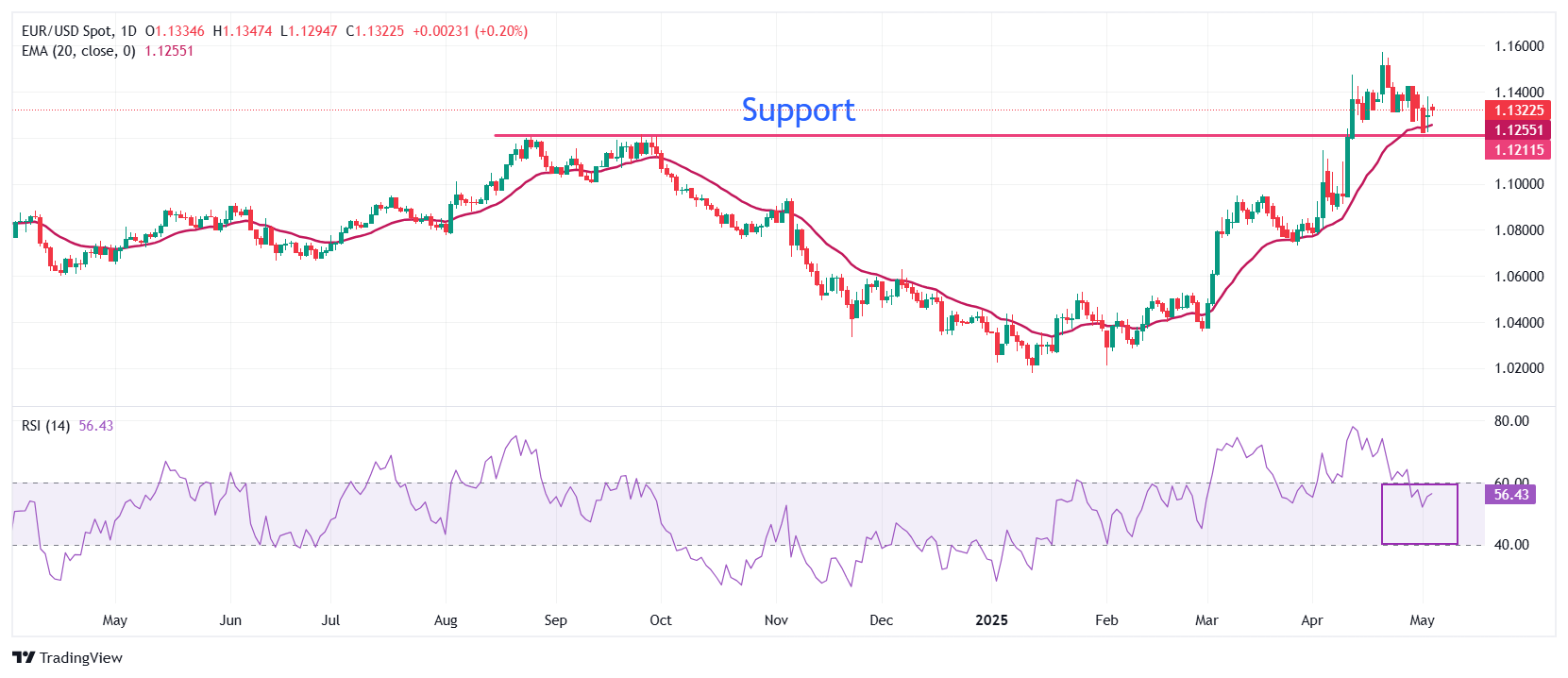
EUR/USD holds recovery above the key level of 1.1300 on Monday from its three-week low of 1.1265 posted on Thursday. The major currency pair rebounded after attracting bids near the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) around 1.1260.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) falls inside the 40.00-60.00 range, indicating that the bullish momentum has concluded for now. However, the upside bias still prevails.
Looking up, the psychological level of 1.1500 will be the major resistance for the pair. Conversely, the 25 September high of 1.1214 will be a key support for the Euro bulls.
Fed FAQs
What does the Federal Reserve do, how does it impact the US Dollar?
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
How often does the Fed hold monetary policy meetings?
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
What is Quantitative Easing (QE) and how does it impact USD?
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
What is Quantitative Tightening (QT) and how does it impact the US Dollar?
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.
